Instant payments: Enormous Potential versus Financial Crime Risks
The world of banking continues to evolve at a breathtaking pace and is becoming ever more competitive. Once a new technology has come to market, banks are faced with a dilemma: do we embrace it and run with it, or do we let our competitors gain a first-mover advantage? Delay implies a commercial risk. But the operational and compliance risks that you take on as a first mover may be even greater.
Given the harmonisation of national payment systems across regions, the focus has shifted to international payments and to improve the overall user experience like speed, cost, reliability and traceability. Therefore, payment processors today are seeing some major developments, with new tools appearing such as SWIFT’s gpi and SEPA’s instant payment. These instant cross border payment initiatives are a prime example of what will become the norm in payments.
The rapid pace of digitalisation of payments brought growing market pressure which have led cross-border payments to undergo significant infrastructure modernisation. The overall trend in digital transactions which are increasing at 6% per year alone in Europe. Total number of traceable transactions in Europe increased from 2013 to 2017: from 113B in 2013 to 144B in 2017 (+27,4%; CAGR +6%)
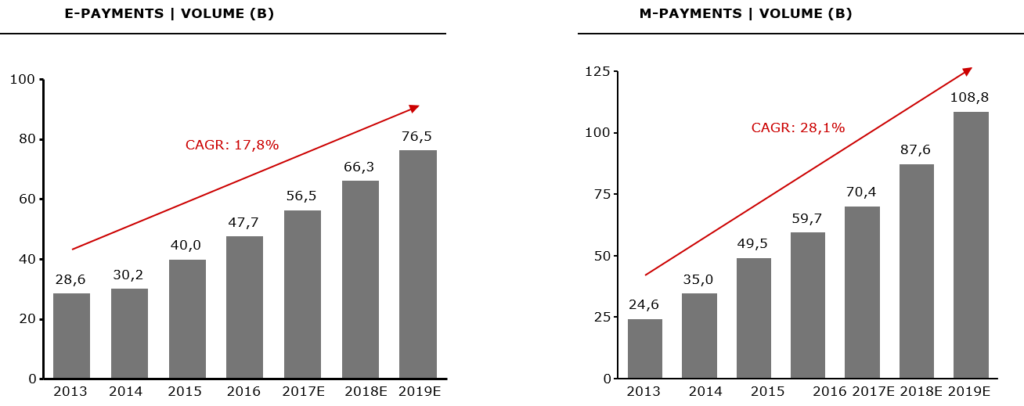
Number of Digital Payments: Global E-Payments increased from 28,6B in 2013 to 56,5B in 2017 (CAGR: 18,6%); Global M-Payments increased from 24,6B in 2013 to 70,4B in 2017 (CAGR: 30,1%)
Banks that offer this service will gain a competitive advantage over banks that don’t provide it. Clients want their payments to be processed quickly because for them it increases efficiency, transparency, convenience, and financial control. For small and medium-sized companies, this form of payment processing helps alleviate liquidity stress and counter party risk. And, in general, people have grown accustomed to things moving fast, so they have little patience and understanding when payment processing is slow.
Instant payment allows sellers and buyers to exchange money and purchase services in seconds. Funds are received in the payee bank account almost immediately, instead of requiring few business days. That can make a significant difference to a small business’s cash flow, in particular, and it means less time spent waiting for money to clear from the buyer’s point of view. Fast transactions are a common requirement in the new economy, especially with increased mobility: the current generations of customers (so-called millennials and beyond) want to be able to make payments anytime, anywhere, using their mobile devices.
So, what’s not to like about instant payment?
Well, quite a lot, actually. Instant payment processing makes it more difficult to detect financial crimes like money laundering and financial fraud. Criminals want to move money as quickly as possible through a number of accounts at different international banks to disguise the origin of funds. There is no faster way to do this than with instant payments. How can a bank possibly detect money laundering activity in a real time world when transaction monitoring is conducted in a batch process needless to mention the more complex criminal activity?
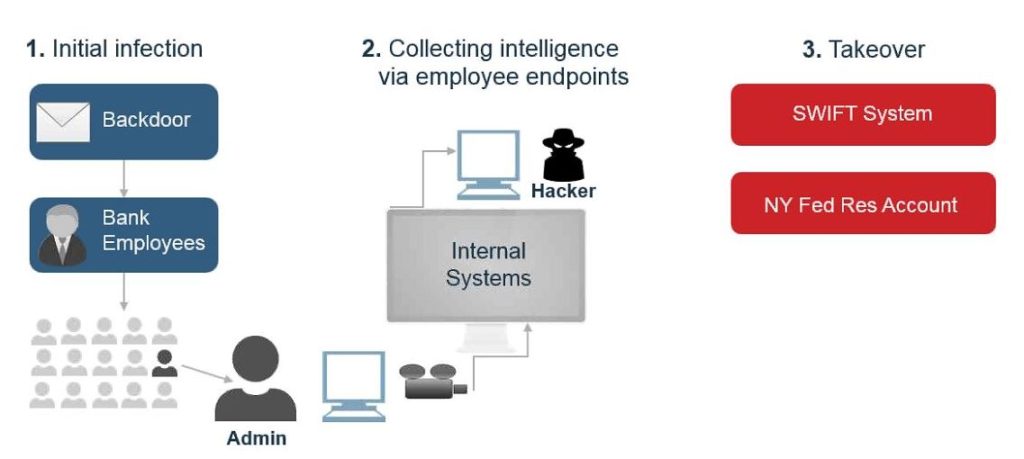
The Bangladesh Bank heist is a perfect illustration of the future complexity involved in monitoring instant payments.
From the $ 81 million stolen from the Bangladesh Bank in February 2016 only $ 15 million has been recovered and there is still no word on who was responsible. Cyber attackers illegally transferred US$ 81 million from the Central Bank of Bangladesh (CBB), to several fictitious bank accounts around the world, by subverting their SWIFT accounts. The hackers used the SWIFT credentials of the CBB to send dozens of fraudulent payments to fake accounts in the Philippines, and other Asian banks. This was without questioned a well-planned attack that used time differences and regional holidays brilliantly.
How will current anti-money laundering systems work in a world of instant payments?
Its difficult enough for financial institutions to monitor against money laundering violations when it takes three to five days for a transaction to be cleared, or at best overnight. With instant payment, the near-impossible becomes totally impossible using conventional methods as transactions clear in a matter of milliseconds. By conventional, we mean here rule-based approaches, where suspicious transactions are put in a queue and investigated in batch mode.
Even in a world operating in batch, traditional AML systems generate too many false positives (typically between two and 15% of all transactions) and therefore imposes a huge workload on banks and investigators.
Number of Suspicious transactions reported to UIF: +51% (’12-16), from 67K in 2012 to 101K in 2016
With instant payment, this problem is greatly increased because banks are under pressure from customers and consumers to clear transactions as quickly as possible in order to meet the agreed level of service.
Transaction monitoring systems built on current technology and based on machine learning offers the only credible answer. By creating algorithms that learn from past results with the expertise and knowledge of AML compliance officers, the system learns to identify false positives, and compliance officers can focus on alerts where there is a higher probability that money laundering is actually occurring.
Another technology-based approach that has been developed recently, called visual mapping, provides insights into how instant payments are moved around. Suspicious payments can be tracked as they move between bank accounts, regardless of whether the payment amount is split between multiple accounts, or those accounts belong to the same or different financial institutions. The software creates a visual map of where and when money has moved, providing new insights and intelligence for fraud and compliance teams to take action.
By bringing together transactional data from multiple financial institutions and running sophisticated algorithms, such solutions can identify the so-called “mule accounts” that are used for money laundering and other illegal activity. Many of these accounts are not set up directly by the criminals themselves but via a number of scams including phishing, spam email, instant messaging etc.
It is worth pointing out that while technology is a necessary condition for successful AML compliance in the new world of instant payment, it is not a sufficient condition. In addition, financial institutions will need to review their compliance procedures and their service offerings to strike the optimum balance between competitiveness and security.
What should be the upper threshold for an instant payment?
Should they give priority to VIP and profitable customers when reviewing suspicious transactions? What about social and political issues? (For example, Muhammad is the world’s most common name, and also appears a lot on sanctions list. But that also means a significantly large number of false positives, which could lead to claims of unfair profiling.) And finally, even with advanced technology and effective redesign of processes and procedures, banks may still need to increase their staffing in order to meet the challenge. They need to ensure that they have enough staff with sufficient knowledge and authority to be available to review transactions quickly.
Some banks have offshored or outsourced simple customer due diligence functions to keep pace. That said, the trend is definitely towards investment in more technology. As a recent article in The Economist put it, “Now, the biggest question for bank controllers is how many humans they can replace with bots without compromising compliance […] Banks are going into partnership with some of the hundreds of ‘Regtechs’ that have sprouted in recent years.” Technology must be a large part of the solution, but banks will just need to take care and seek expert independent advice in reviewing the new Regtech apps: the regulators and the markets will penalize them should their techno-experiments fail.[1]
For more articles on financial crime and Anti-Money Laundering join the AML Knowledge Centre at https://www.linkedin.com/groups/8196279/
[1] “The past decade has brought a compliance boom in banking”, Economist 2 May 2019.






